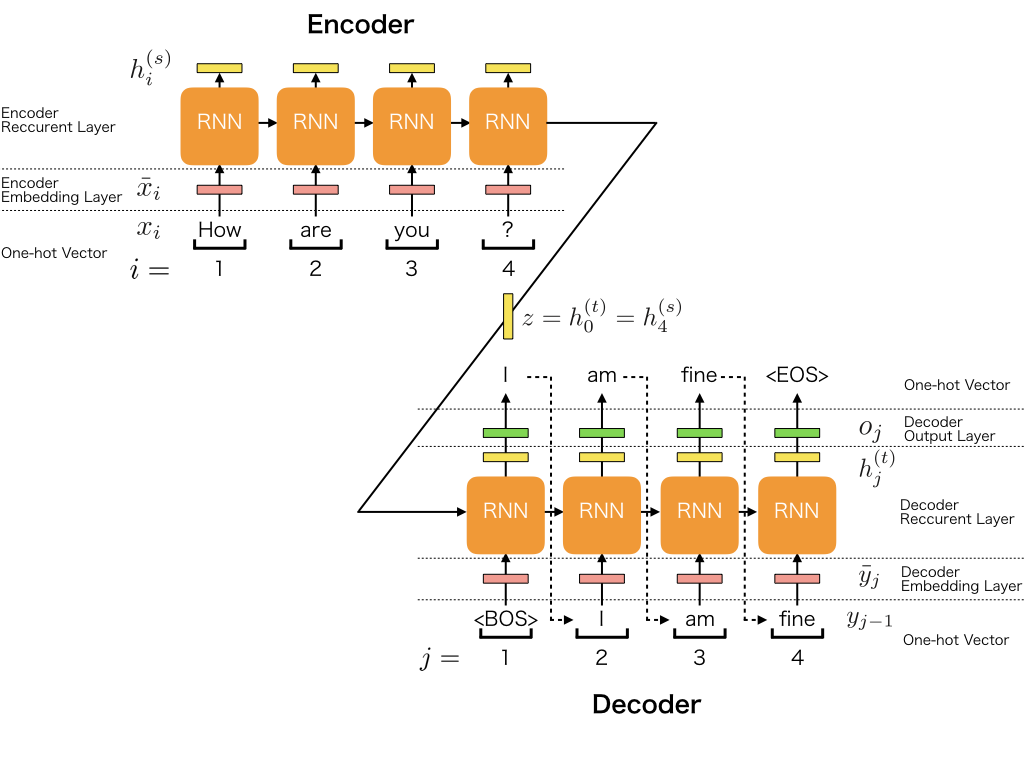
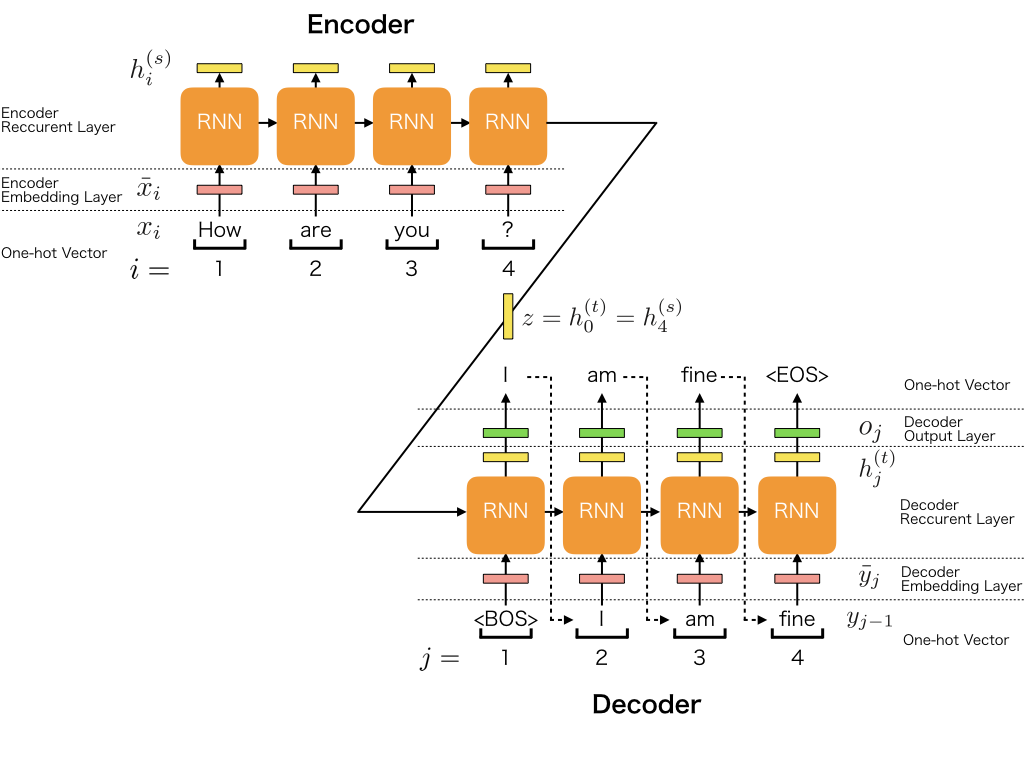
seq2seq¶
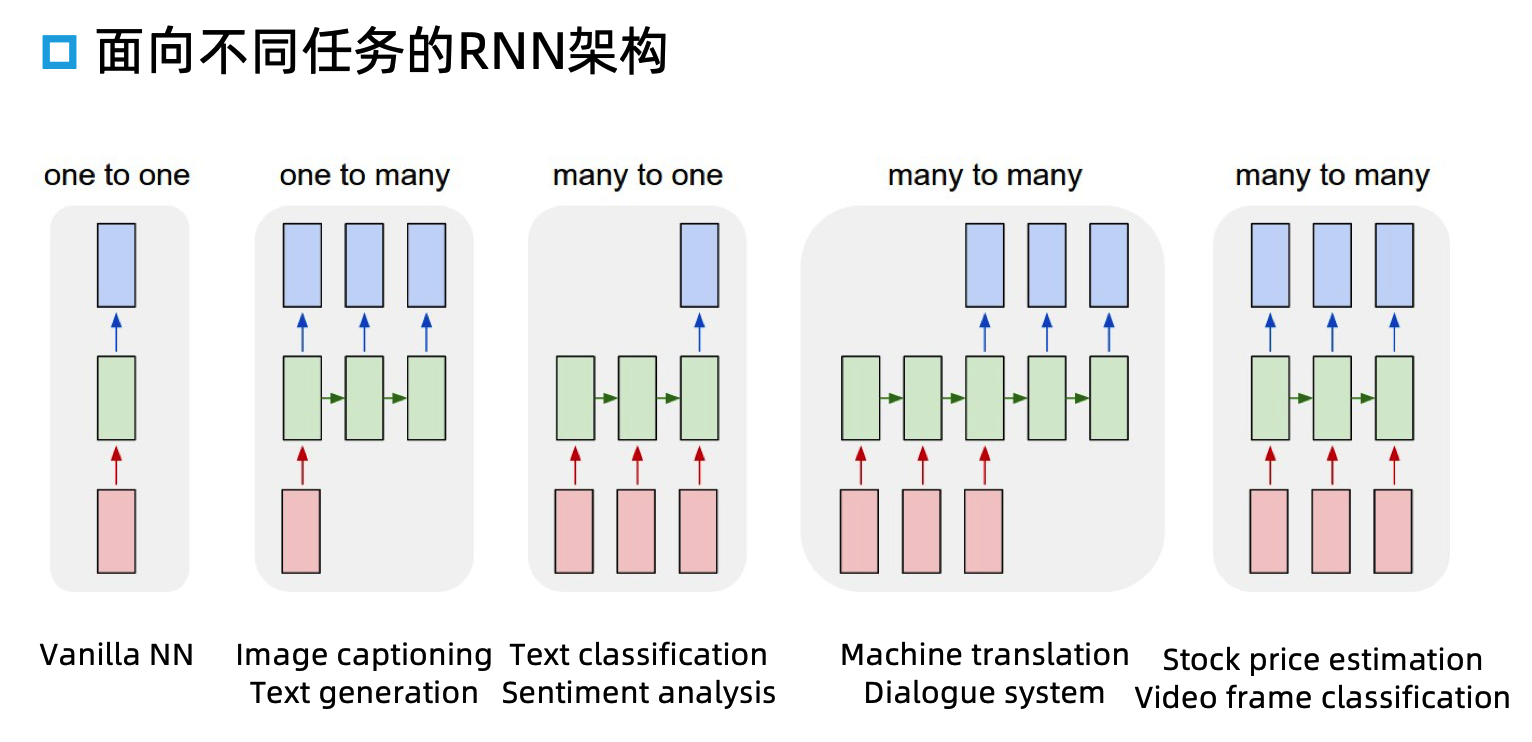
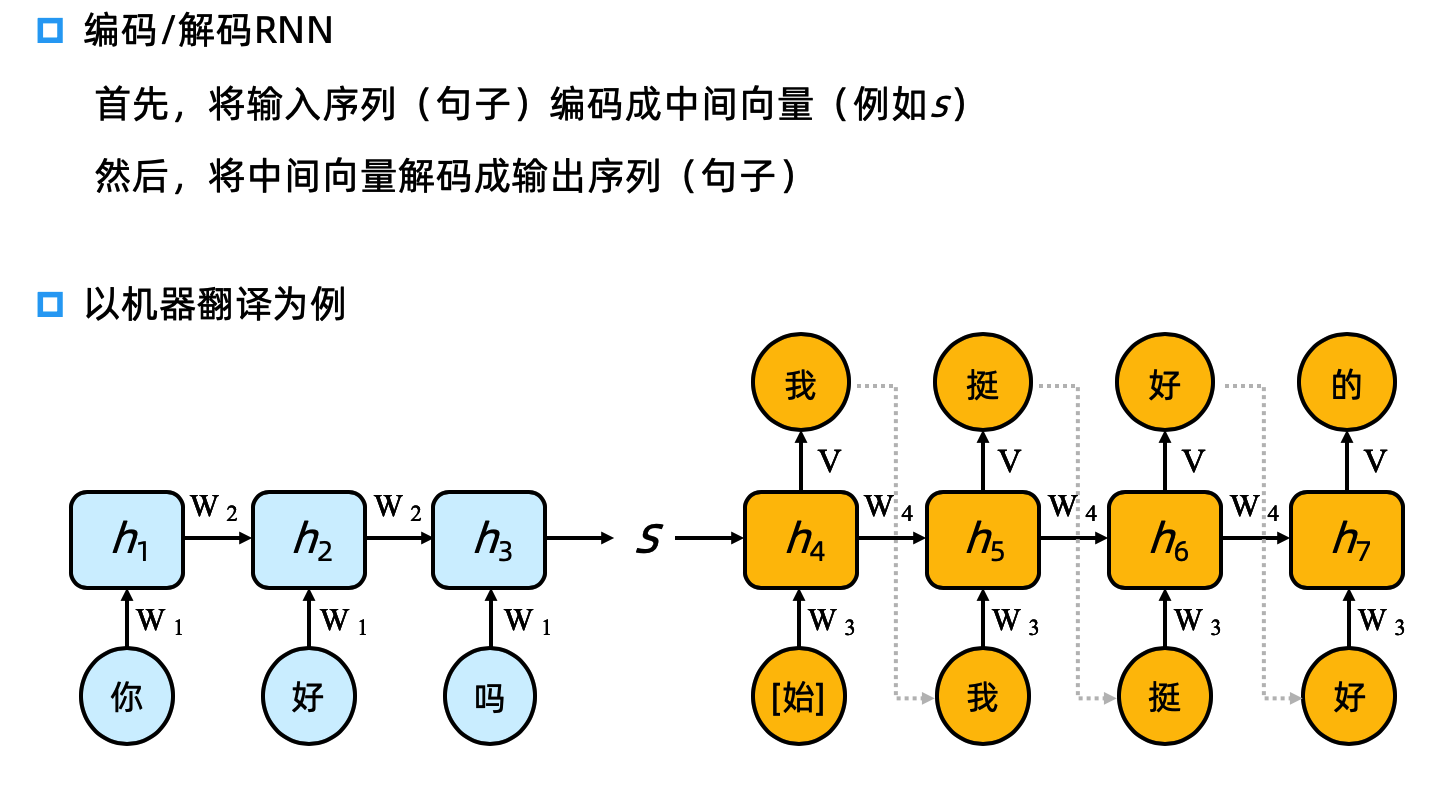
In [1]:
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Input, LSTM, Dense, Embedding
from keras.optimizers import Adam
import numpy as np
In [2]:
batch_size = 64
epochs = 9
latent_dim = 256
embedding_size = 128
file_name = '../input/poetry.txt'
In [3]:
input_texts = []
target_texts = []
input_vocab = set()
target_vocab = set()
with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
# 将诗句用逗号分开
line_sp = line.strip().split(',')
# 如果诗中不含逗号,这句诗我们就不用了
if len(line_sp) < 2:
continue
# 上句为input_text,下句为target_text
input_text, target_text = line_sp[0], line_sp[1]
# 在下句前后开始字符和结束字符
target_text = '\t' + target_text[:-1] + '\n'
input_texts.append(input_text)
target_texts.append(target_text)
# 统计输入侧的词汇表和输出侧的词汇表
for ch in input_text:
if ch not in input_vocab:
input_vocab.add(ch)
for ch in target_text:
if ch not in target_vocab:
target_vocab.add(ch)
# 建立字典和反向字典
input_vocab = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(input_vocab)])
target_vocab = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(target_vocab)])
reverse_input_char_index = dict((i, char) for char, i in input_vocab.items())
reverse_target_char_index = dict((i, char) for char, i in target_vocab.items())
# 输入侧词汇表大小
encoder_vocab_size = len(input_vocab)
# 最长输入句子长度
encoder_len = max([len(sentence) for sentence in input_texts])
# 输出侧词汇表大小
decoder_vocab_size = len(target_vocab)
# 最长输出句子长度
decoder_len = max([len(sentence) for sentence in target_texts])
print(encoder_vocab_size)
print(encoder_len)
print(decoder_vocab_size)
print(decoder_len)
In [4]:
encoder_input_data = np.zeros((len(input_texts), encoder_len), dtype='int')
decoder_input_data = np.zeros((len(input_texts), decoder_len), dtype='int')
decoder_target_data = np.zeros((len(input_texts), decoder_len, 1), dtype='int')
for i, (input_text, target_text) in enumerate(zip(input_texts, target_texts)):
for t, char in enumerate(input_text):
encoder_input_data[i, t] = input_vocab[char]
for t, char in enumerate(target_text):
decoder_input_data[i, t] = target_vocab[char]
if t > 0:
decoder_target_data[i, t - 1, 0] = target_vocab[char]
print(encoder_input_data.shape)
print(decoder_input_data.shape)
print(decoder_target_data.shape)
下面这段代码用于搭建模型¶
In [5]:
# 编码器输入层
encoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None,))
# 编码器词嵌入层
encoder_embedding = Embedding(input_dim=encoder_vocab_size, output_dim=embedding_size, trainable=True)(encoder_inputs)
# 编码器长短期记忆网络层
encoder = LSTM(latent_dim, return_state=True)
# 编码器长短期记忆网络输出是一个三元组(encoder_outputs, state_h, state_c)
# encoder_outputs是长短期记忆网络每个时刻的输出构成的序列
# state_h和state_c是长短期记忆网络最后一个时刻的隐状态和细胞状态
encoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = encoder(encoder_embedding)
# 我们会把state_h和state_c作为解码器长短期记忆网络的初始状态,之前我们所说的状态向量的传递就是这样实现的
encoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
# 解码器网络建构
# 解码器输入层
decoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None,))
# 解码器词嵌入层
decoder_embedding = Embedding(input_dim=decoder_vocab_size, output_dim=embedding_size, trainable=True)(decoder_inputs)
# 解码器长短期记忆网络层
decoder_lstm = LSTM(latent_dim, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
# 解码器长短期记忆网络的输出也是三元组,但我们只关心三元组的第一维,同时我们在这里设置了解码器长短期记忆网络的初始状态
decoder_outputs, _, _ = decoder_lstm(decoder_embedding, initial_state=encoder_states)
# 解码器输出经过一个隐层softmax变换转换为对各类别的概率估计
decoder_dense = Dense(decoder_vocab_size, activation='softmax')
# 解码器输出层
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs)
# 总模型,接受编码器和解码器输入,得到解码器长短期记忆网络输出
model = Model([encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs], decoder_outputs)
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001), loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy')
model.summary()
训练模型¶
In [6]:
model.fit([encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data], decoder_target_data, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs, validation_split=0.2)
Out[6]:
这里可能同学们会很困惑,为什么下面这段代码又在构建模型,原因是seq2seq在训练和生成的时候并不完全相同¶
训练的时候,解码器是有预先输入的,我们会把正确的下句作为输入指导解码器进行学习,具体来说,不管上一个时刻解码器的输出是什么,我们都用预先给定的输入作为本时刻的输入¶
这种训练方式称为Teacher forcing¶
但是在生成的时候,解码器是没有预先输入的,我们会把上一个时刻解码器的输出作为本时刻的输入,如此迭代的生成句子¶
训练的时候我们的model是一整个seq2seq的模型,这个黑盒在给定encoder_input和decoder_input的情况下可以产生对应的输出¶
但是生成时我们没有decoder_input,我们就把黑盒拆成两个黑盒,一个是编码器,一个是解码器,方便我们的操作¶
In [7]:
# 第一个黑盒,编码器,给定encoder_inputs,得到encoder的状态
encoder_model = Model(encoder_inputs, encoder_states)
# 第二个黑盒,解码器
# 解码器接受三个输入,两个是初始状态,一个是之前已经生成的文本
decoder_state_input_h = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_state_input_c = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_states_inputs = [decoder_state_input_h, decoder_state_input_c]
# 解码器产生三个输出,两个当前状态,一个是每个时刻的输出,其中最后一个时刻的输出可以用来计算下一个字
decoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = decoder_lstm(decoder_embedding, initial_state=decoder_states_inputs)
decoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs)
decoder_model = Model([decoder_inputs] + decoder_states_inputs, [decoder_outputs] + decoder_states)
In [8]:
def decode_sequence(input_seq):
# 先把上句输入编码器得到编码的中间向量,这个中间向量将是解码器的初始状态向量
states_value = encoder_model.predict(input_seq)
# 初始的解码器输入是开始符'\t'
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1))
target_seq[0, 0] = target_vocab['\t']
stop_condition = False
decoded_sentence = ''
# 迭代解码
while not stop_condition:
# 把当前的解码器输入和当前的解码器状态向量送进解码器
# 得到对下一个时刻的预测和新的解码器状态向量
output_tokens, h, c = decoder_model.predict([target_seq] + states_value)
# 采样出概率最大的那个字作为下一个时刻的输入
sampled_token_index = np.argmax(output_tokens[0, -1, :])
sampled_char = reverse_target_char_index[sampled_token_index]
decoded_sentence += sampled_char
# 如果采样到了结束符或者生成的句子长度超过了decoder_len,就停止生成
if (sampled_char == '\n' or len(decoded_sentence) > decoder_len):
stop_condition = True
# 否则我们更新下一个时刻的解码器输入和解码器状态向量
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1))
target_seq[0, 0] = sampled_token_index
states_value = [h, c]
return decoded_sentence
In [9]:
for seq_index in range(200, 300):
input_seq = encoder_input_data[seq_index: seq_index + 1]
decoded_sentence = decode_sequence(input_seq)
print('-')
print('Input sentence:', input_texts[seq_index])
print('Decoded sentence:', decoded_sentence)